[email protected]
+91 9019666757
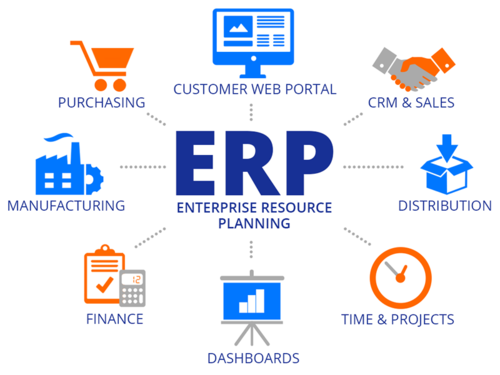
What is
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
At its
core, an ERP is an application that automates business processes, and provides
insights and internal controls, drawing on a central database that collects
inputs from departments including accounting, manufacturing, supply chain
management, sales, marketing and human resources (HR).
Once
information is compiled in that central database, leaders gain
cross-departmental visibility that empowers them to analyze various scenarios,
discover process improvements and generate major efficiency gains. That
translates to cost savings and better productivity as people spend less time
digging for needed data.
ERP
software that’s tailored to meet the needs of an individual business pays major
dividends, making these systems a critical tool for companies across industries
and of all sizes. Many of the world’s best-known and most successful firms have
leaned on ERP for the last quarter century. Now, this software can be
configured and priced to meet the needs of all-size businesses.
Put
simply, an ERP system helps unify people, core business processes and
technology across an organization.
Why Is
ERP Important for Businesses?
ERP
systems have become table stakes for businesses looking to use resources
wisely. They can help leaders reallocate human and financial capital or build
more efficient core business processes that save money without sacrificing on
quality or performance.
An ERP is
also an asset when it comes to planning and coordination. Employees can see
current available inventory and customer orders in detail, then compare
supplier purchase orders and forecasted future demand. If necessary, they can
make adjustments to head off problems. ERP software improves communication and
collaboration as well because workers can check on the status of other
departments to guide their own decisions.
As a
comprehensive source of data, an ERP system also provides a host of reports and
analytics that can be difference-makers for the business. Turning a vast trove
of information into charts and graphs that clearly illustrate trends and help
model possible results is an ERP capability executives find invaluable.
How Can
ERP Improve or Help a Business?
ERP
enables companies to identify areas of the business with room for improvement
or opportunities for expansion. User uptake is key: The more employees with
access, the more likely teams will spot problems, whether a spike in demand for
a certain product, late shipments from a supplier or an impending cash flow
crunch. Employees can then proactively mitigate the issue to the extent
possible.
Executives
are generally focused on outcomes — using information to achieve objectives,
like increasing efficiency, reducing costs and responding to changing consumer
needs or market conditions.
For
business units, ERP software can automate many error-prone tasks, like account
reconciliations, customer billing and order processing, and provide the information
teams need to operate more efficiently.
But the
real beauty of ERP is that it can give both a 10,000-foot view of the company’s
health and detailed insights into a specific process or KPI by not only storing
and organizing data, but identifying patterns and flagging anomalies that
require investigation. Try that with a spreadsheet.
Other
business upsides:
Access to
data from anywhere
Employees
no longer need to shuffle through piles of papers or files scattered across a
desktop. With cloud-based ERP, a warehouse manager can log in from a mobile
device while on the shop floor, or a salesperson can check inventory while at a
customer site.
Information
is always up-to-date
Because
the ERP system is continually receiving information from various departments,
it’s updated immediately as inventory is pulled, a payment is posted or emails
are sent to customers. This provides a major advantage because decision-makers
are basing their choices on up-to-the-minute data.
Business
decisions based on the same data
With a
common database, all decision-makers are on the same page. There are no
duplicate or conflicting sources of information, and companies have the ability
schedule and distribute dynamic reports automatically. Need more depth?
Underlying data can be accessed simply by clicking the report.
12
Benefits of ERP Systems
Today’s
ERP solutions have rich feature sets that bring countless benefits to
businesses. While what an individual firm sees as the greatest value of this
technology will vary, here are key universal advantages ERP delivers:
1. Cost
savings:
Perhaps
the biggest value proposition of ERP systems is they can save your organization
money in a number of ways. By automating many simple, repetitive tasks, you
minimize errors and the need to add employees at the same rate as business
growth. Cross-company visibility makes it easier to spot inefficiencies that
drive up costs and leads to better deployment of all resources, from labor to
inventory to equipment. And with cloud ERP, companies may quickly see
incremental value from the software, over and above what they’re spending.
2.
Workflow visibility:
With all
workflows and information in one place, employees with access to the system can
see the status of projects and the performance of different business functions
relevant to their jobs. This visibility may be particularly valuable to
managers and leaders, and it’s far faster and easier than searching for the
right documents and constantly asking colleagues for updates.
3.
Reporting/analytics:
Data is
useful only if companies can analyze and understand it, and an ERP helps with
that. Leading solutions have impressive reporting and analytics tools that
allow users to not only track KPIs, but display any metrics or comparisons they
can dream up. Since an ERP is all-encompassing, it can help a business
understand how a change or problem with a process in one department affects the
rest of the company.
4.
Business insights/intelligence:
Because
ERPs can access real-time data from across the company, these systems can
uncover impactful trends and provide extensive business insights. This leads to
better decision-making by organizational leaders who now have easy access to
all relevant data.
5.
Regulatory compliance & data security:
Financial
reporting standards and governmental and industry-specific data security regulations
change frequently, and an ERP can help your company stay safe and compliant. An
ERP provides an audit trail by tracking the lifecycle of each transaction,
including adherence to required approval workflows. Businesses may also reduce
the chance of errors and related compliance snafus with automation. ERP
software provides financial reports that comply with standards and regulations,
and SaaS applications are well-equipped to help companies with PCI-DSS
compliance.
6. Risk
management:
ERP
technology reduces risk in a few ways. Granular access control and defined
approval workflows can strengthen financial controls and reduce fraud.
Additionally, more-accurate data heads off mistakes that could lead to lost
sales or fines. And finally, the ability to see the status of the entire
operation enables employees to quickly handle risks posed by business
disruptions.
7. Data
security:
ERP
providers understand that your system houses critical, sensitive data and take
necessary steps to ensure it is secure. This diligence is more important than
ever as the volume and scale of cyberattacks increase. Cloud ERP software, in
particular, uses cutting-edge security protocols to ensure your company doesn’t
fall victim to a damaging attack.
8.
Collaboration:
Employees
are most effective when they work together. ERP solutions make it easy to share
information — like purchase orders, contracts and customer-support records —
among teams. It knocks down walls between departments by giving employees
appropriate access to real-time data on related business functions.
9.
Scalability:
The right
ERP system will be scalable and flexible enough to meet your company’s needs
today and for the foreseeable future. Cloud systems in particular adapt to
minor and major operational changes even as the amount of data the organization
captures and demand for access increase.
10.
Flexibility:
While ERP
software helps businesses follow best practices, it also offers the flexibility
to support unique processes and objectives. The system gives administrators the
ability to build out company-specific workflows and create automatic reports
important to different departments and executives. An ERP enhances your
organization’s innovation and creativity.
11.
Customization:
While
most companies find that modern ERPs support their businesses “out of the box,”
some firms need to add to the extensive built-in functionality. If you have a
lot of specialized processes, look for an extensible system that allows your
integrator or IT staff to write code that adds needed features, or that can
integrate with homegrown or legacy solutions. However, before going the custom
route, take a close look at your processes — the prebuilt functionality and
configurations modern ERP solutions support are based on best practices
gathered from thousands of companies. Aim to minimize customizations.
12.
Customer & partner management:
An ERP
can strengthen a company’s partner and customer relationships. It can provide
insights on suppliers, shipping carriers and service providers, with the cloud
enabling even better, more convenient information exchange. When it comes to
customers, the solution can track survey responses, support tickets, returns
and more so the organization can keep its finger on the pulse of customer
satisfaction.
